PyQt5를 이용한 GUI 오목앱 만들기
개요
오목게임을 파이썬을 이용해 만들어본 예제입니다.
GUI 앱을 처음 시도해보는 초보가가 공부하기 좋은 예제라고 생각합니다.
개발환경
- Windows 11 Pro, Visual Studio 2022
- Python 3.9 64bit, PyQt5 5.15.4
소스코드
두개의 파이썬 파일 (*.py) 로 구성되어 있으며 (main.py, game.py),
main.py 를 시작파일로 설정하고 진행.
main.py
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QMessageBox
from PyQt5.QtCore import Qt
from PyQt5.QtGui import QPainter
from game import Omok
import sys
QApplication.setAttribute(Qt.AA_EnableHighDpiScaling, True)
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle('Ocean Coding School')
self.setFixedSize(600,600)
self.omok = Omok(self)
def paintEvent(self, e):
qp = QPainter()
qp.begin(self)
self.omok.draw(qp)
qp.end()
def mousePressEvent(self, e):
self.omok.mouseDown( e.x(), e.y() )
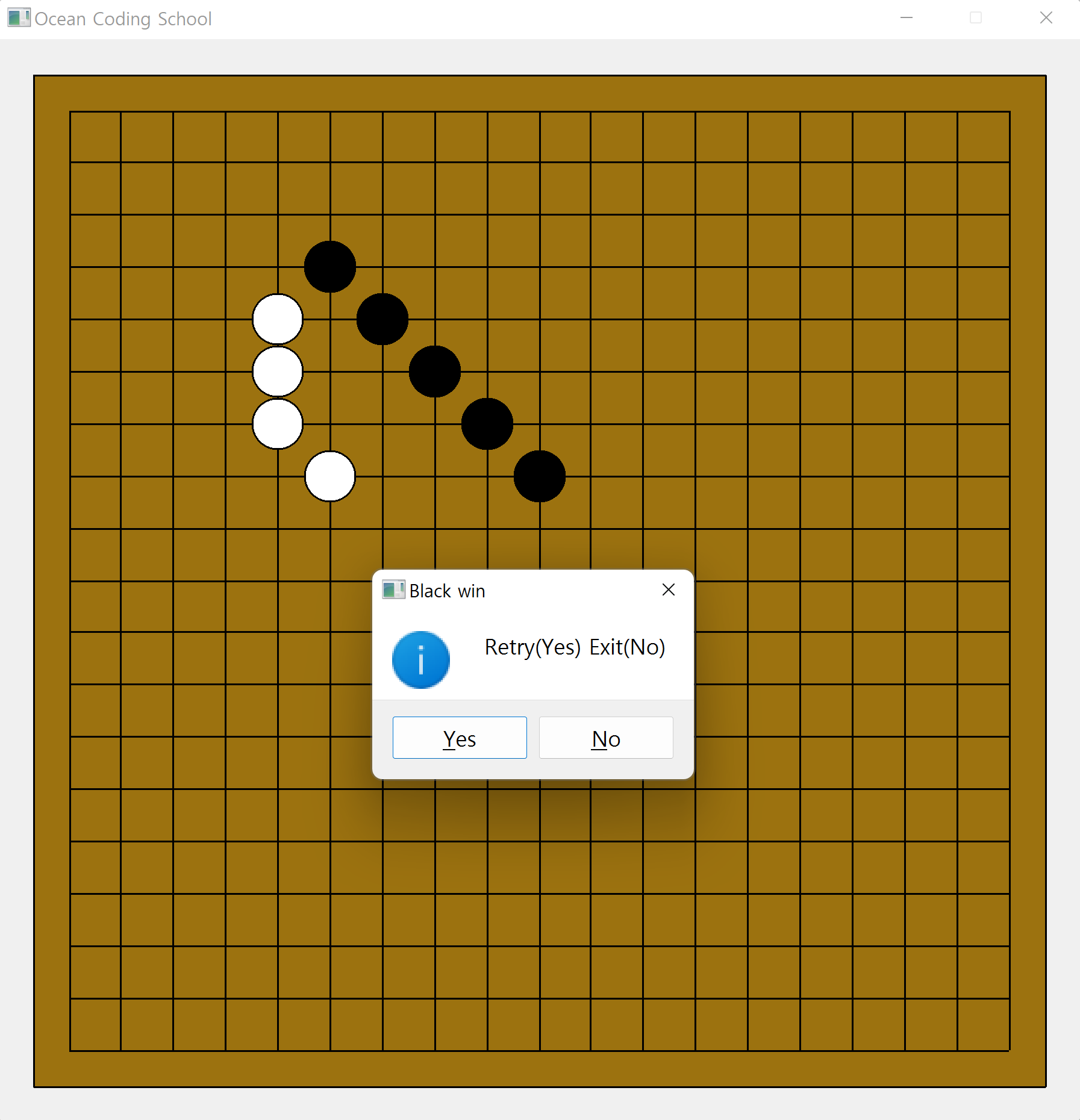
def gameOver(self, w):
if w==1:
winner = 'Black win'
elif w==2:
winner = 'White win'
else:
winner = 'Draw'
yesno = QMessageBox.information(self, winner, 'Retry(Yes) Exit(No)',
QMessageBox.Yes | QMessageBox.No)
if yesno==QMessageBox.Yes:
del(self.omok)
self.omok = Omok(self)
else:
self.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
w = Window()
w.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
[라인 1~7]
PyQt5 모듈에서 필요한 클래스를 import 하는 구문.
7번 라인은 모니터 픽셀의 밀도를 자동으로 증가시키는 코드로, 4K모니터 사용시 유용.
자세한 내용은 아래의 Qt Documenation 참조.
[라인 11~16]
QWidget에서 상속받은 Window 클래스의 생성자 함수.
뒤에서 설명할 game.py 파일에 선언된 Omok Class 의 객체를 생성.
실제 오목게임이 그려지고 진행되는 것은 Omok 클래스가 담당, Window 클래스는 창만 생성하고 게임의 역할은 game.py로 코드를 분산하는 구조를 가지도록 설계.
[라인 18~22]
Qt의 QWidget Class에 선언된 함수의 재정의 (Override).
위젯을 새로 그려야 할 필요가 있을 때 마다 호출되는 함수.
그림을 그릴 QPainter 객체를 생성하고, Omok Class의 draw() 전달인자로 넘겨 실제 그림을 그리는 곳은 Omok 클래스가 담당하도록 유도.
[라인 24~25]
마찬가지로 Qt의 QWidget Class에 선언된 함수의 재정의 (Override).
마우스를 클릭한 좌표를 Omok Class로 알려주고 처리하도록 유도.
[라인 27~42]
오목게임의 종료 시 (흑승, 백승, 무승부),
game.py에 선언된 Omok Class에서 보내는 종료신호, End Signal 발생.
이 Signal과 연결된 Slot Function 으로 게임의 승자를 메시지박스로 출력.
참고로 Qt에서는 Signal이 발생될 때 호출되는 Callback Function을 슬롯함수라고 부름.
[라인 45~49]
Python 코드의 메인함수, 시작점.
game.py
from PyQt5.QtCore import QRect, QObject, pyqtSignal
from PyQt5.QtGui import QColor, QBrush
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMessageBox
class Omok(QObject):
end_signal = pyqtSignal(int)
def __init__(self, w):
super().__init__()
self.parent = w
self.end_signal.connect(self.parent.gameOver)
self.rect = w.rect()
self.outrect = QRect(self.rect)
gap = 20
self.outrect.adjust(gap, gap, -gap, -gap)
self.inrect = QRect(self.outrect)
gap = 20
self.inrect.adjust(gap, gap, -gap, -gap)
self.line = 19
self.size = self.inrect.height() / (self.line-1)
self.bdol = []
self.wdol = []
self.bturn = True
# 0:None, 1:Black, 2:White
self.map = [[0 for _ in range(self.line)] for _ in range(self.line)]
#print(self.map)
def draw(self, qp):
# board
b = QBrush( QColor(156,114,15))
qp.setBrush(b)
qp.drawRect(self.outrect)
# line
x = self.inrect.left()
y = self.inrect.top()
x1 = self.inrect.right()
y1 = self.inrect.top()
x2 = self.inrect.left()
y2 = self.inrect.bottom()
for i in range(self.line):
qp.drawLine(x, y+self.size*i, x1, y1+self.size*i)
qp.drawLine(x+self.size*i, y, x2+self.size*i, y2)
# stone
b = QBrush(QColor(0,0,0))
qp.setBrush(b)
for rect in self.bdol:
qp.drawEllipse(rect)
b = QBrush(QColor(255,255,255))
qp.setBrush(b)
for rect in self.wdol:
qp.drawEllipse(rect)
def mouseDown(self, x, y):
if self.inrect.contains(x, y):
r, c = self.findRowCol(x, y)
#print(r,c)
if self.map[r][c]==0:
L = (self.inrect.left()-self.size//2) + c*self.size
T = (self.inrect.top()- self.size//2) + r*self.size
rect = QRect(L, T, self.size, self.size)
if self.bturn:
self.map[r][c] = 1
self.bdol.append(rect)
else:
self.map[r][c] = 2
self.wdol.append(rect)
self.bturn = not self.bturn
self.parent.update()
w = self.findWinner()
if w>0:
self.end_signal.emit(w)
else:
QMessageBox.warning(self.parent, 'Error', 'Already laid', QMessageBox.Ok)
else:
QMessageBox.warning(self.parent, 'Error', 'Click inside a board', QMessageBox.Ok)
def findRowCol(self, x, y):
r = (y-self.inrect.top()-self.size//2) // self.size
c = (x-self.inrect.left()-self.size//2) // self.size
return int(r+1), int(c+1)
# 0:continue, 1:Black win, 2:White win, 3:Draw
def findWinner(self):
cnt = 5
empty = 0
for r in range(self.line):
for c in range(self.line):
if self.map[r][c]==0:
empty+=1
b = [0,0,0,0]
w = [0,0,0,0]
for i in range(cnt):
if c+i<self.line and self.map[r][c+i]==1:
b[0]+=1
if r+i<self.line and self.map[r+i][c]==1:
b[1]+=1
if (c+i<self.line and r+i<self.line) and self.map[r+i][c+i]==1:
b[2]+=1
if (c-i>=0 and r+i<self.line) and self.map[r+i][c-1]==1:
b[3]+=1
for i in range(cnt):
if c+i<self.line and self.map[r][c+i]==2:
w[0]+=1
if r+i<self.line and self.map[r+i][c]==2:
w[1]+=1
if (c+i<self.line and r+i<self.line) and self.map[r+i][c+i]==2:
w[2]+=1
if (c-i>=0 and r+i<self.line) and self.map[r+i][c-1]==2:
w[3]+=1
for i in b:
if i>=cnt: return 1;
for i in w:
if i>=cnt: return 2;
if empty==0:
return 3 #draw
return 0
[라인 9~33]
Omok Class의 생성자함수.
전달인자로 받은 위젯정보를 저장하고, 오목 게임에 필요한 변수 생성 등 초기화를 수행.
2차원 리스트로 생성된 self.map 은 향후 오목게임이 진행될 때 바둑판에 놓여진 돌의 상태를 저장. (빈곳:0, 흑돌:1, 백돌:2)
아래 그림은 상태를 저장할 2차원 리스트를 출력해본 모습이며 아직 바둑판에
놓여진 돌은 없다.
[라인 36~63]
앞서 설명한 main.py의 paintEvent() 에 의해 호출되는 함수.
전달인자로 받은 QPainter 객체를 이용해 바둑판의 선, 바둑돌을 그리는 역할을 담당.
[라인 65~91]
앞서 설명한 main.py의 mousePressEvent() 에 의해 호출되는 함수.
바둑판을 클릭한 좌표를 이용, 클릭한 위치와 가장 가까운 바둑판 교차점의 행,열 값 을 찾아낸다.
만약 그곳에 돌이 놓여져 있지 않다면, 바둑돌이 그려질 사각형 좌표를 생성해 흑돌, 백돌 리스트에 저장.
흑돌, 백돌의 순서를 바꾸고 판정함수를 호출해 승패를 검사.
[라인 93~96]
위젯을 마우스로 클릭한 좌표를 기준으로 가장 가까운 교차점의 행,열을 반환하는 함수.
[라인 100~139]
바둑돌을 놓을때마다 호출되는 판정함수. 리턴값은 아래 넷 중 하나이다.
(진행중:0, 흑승:1, 백승:2, 무승부:3)
각 색깔의 돌들이 가로, 세로, 대각선 두 방향으로 5개가 연속되는지 체크.
만약 바둑판의 모든 곳에 바둑돌이 다 놓여져 있다면 무승부로 판단.
이상으로 모든 설명을 마칩니다.
감사합니다.




흥미로운 글이었습니다. 따라해보는 것도 재미있네요.
답글삭제실력이 금방 늘 것 같습니다.
앞으로도 재밌는 글 부탁드립니다~
안녕하세요.
삭제다른사람이 만든 코드라도 이해되면 내 것(지식)이라 생각합니다.
말씀하신것처럼 그러다보면 실력이 늡니다.
감사합니다.
우와
답글삭제